Reducto 和 RAG-Anything 都利用视觉-语言模型(VLM)来增强对多模态文档的理解,确保图像、表格等非文本内容被转化为 LLM-ready 的数据 或整合为上下文以提供更深入的洞察。然而,两者在架构、目的和 VLM 实施重点上存在显著差异。
1. 架构焦点与系统性质
| 特性 (Feature) | Reducto | RAG-Anything |
|---|---|---|
| 性质 (Nature) | 商业产品/服务,被描述为“AI 文档解析和提取软件”,通过灵活的 API 提供,面向生产环境的 AI。 | 开源 RAG 框架,是建立在 LightRAG 之上的“一体化多模态文档处理 RAG 系统”。 |
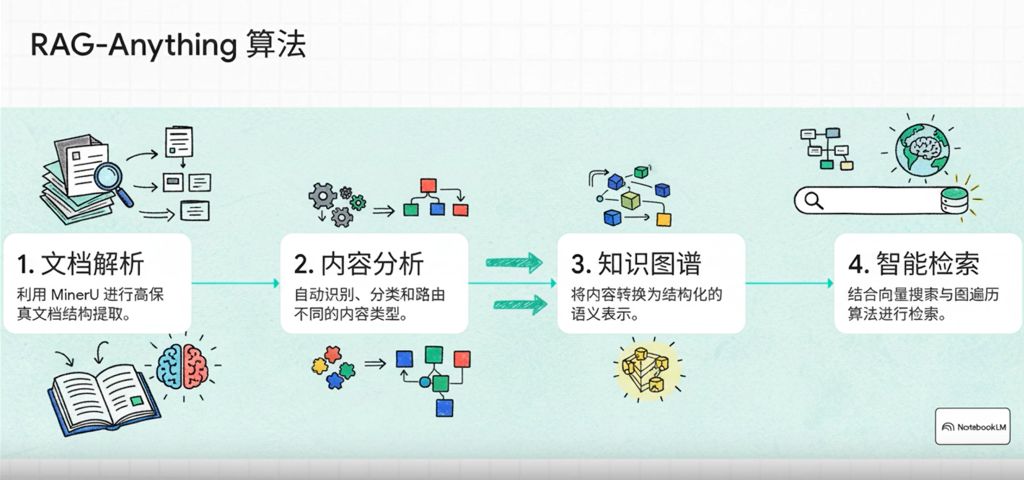
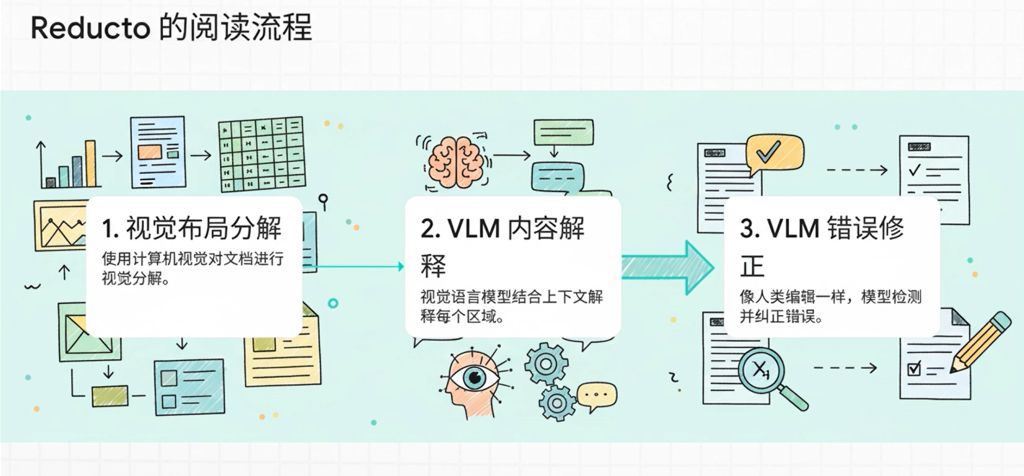
| 核心流程 (Core Pipeline) | 使用多程(multi-pass)系统:首先是传统计算机视觉(CV)进行文档分解,然后是 VLM 解释,以及 VLM/Agentic 模型进行校正。 | 实施多阶段多模态流水线:文档解析 → 内容分析 → 知识图谱 → 智能检索。 |
| 企业就绪性 (Enterprise Readiness) | 专为生产 AI 而设计,获得财富 10 强企业的信任,具备 99.9%+ 运行时间、企业级支持、以及 SOC2 和 HIPAA 合规认证。可完全部署在用户自己的基础设施内。 | 专注于提供灵活的 RAG 框架。要求用户自行配置依赖项(例如,处理 Office 文档需要 LibreOffice)和外部模型(例如,需要配置 vision_model_func 以使用 GPT-4o 等 VLM)。 |
2. VLM 利用与多模态处理
Reducto 的 VLM 方法:校正与解释
Reducto 的系统主要在文档提取的内容分析和细化阶段使用 VLM。
- 布局分割(CV 优先): 传统计算机视觉模型首先从视觉上分解文档,捕获区域、表格、图形和文本。
- 上下文解释(VLM): VLM 随后在上下文中解释每个识别出的区域,进行诸如将标签链接到数值、理解表格和分类段落的任务。
- 准确性增强(Agentic 模型/VLM): Reducto 具有一个Agentic 模型,它能检测并纠正细微错误,“像人类编辑一样”工作,确保在最详细的案例中也能保证准确性。Reducto 的目标是产生最准确、LLM-ready 的结果。
RAG-Anything 的 VLM 方法:查询和关系建模
RAG-Anything 在内容处理阶段和检索查询阶段都使用了 VLM:
- 内容分析器(Visual Content Analyzer): 专用的视觉内容分析器集成了视觉模型,根据视觉语义生成上下文感知的描述性说明文字(captions)。
- 增强查询(VLM-Enhanced Query Mode): RAG-Anything 现已推出 VLM 增强查询模式。当查询包含图像的文档时,系统会自动:
- 检索包含图像路径的相关上下文。
- 加载并将图像编码为 Base64 格式。
- 将文本上下文和图像一起发送给 VLM (例如,配置为 GPT-4o),进行综合多模态分析,从而结合视觉和文本上下文以获得更深入的见解。用户可以手动或自动控制此 VLM 增强功能。
- 多模态知识图谱: RAG-Anything 通过多模态知识图谱索引将文档内容转化为结构化语义表示。该过程涉及跨模态关系映射,以建立文本实体与多模态组件之间的语义连接和依赖关系。
3. 输出结构与内容范围
| 特性 (Feature) | Reducto | RAG-Anything |
|---|---|---|
| 数据结构化 | 专注于 LLM 优化,包括智能分块 (Intelligent chunking)、图表总结 (Figure summarization)、图表提取 (Graph extraction) 和嵌入优化 (Embedding optimization)。 | 专注于多模态知识图谱,通过多模态实体提取和跨模态关系映射来维护内容间的语义和结构关系。 |
| 支持内容 | 支持 PDFs、图像、电子表格、幻灯片等文件类型。可处理复杂的文档,如投资者资料、SEC 文件、复杂的表格、图表和财务报表。 | 支持 PDFs、Office 文档(DOC/DOCX/PPT/PPTX/XLS/XLSX)、图像和文本文件(TXT/MD)。具有针对图像、表格和数学公式(支持原生 LaTeX 格式)的专用内容处理器。 |
| 语言支持 | 提供超过 100 种语言的多语言解析。 | (来源未明确提及广泛的多语言支持范围,但 MinerU 解析器支持设置 lang 参数进行 OCR 优化,例如“ch”或“ja”。) |
详细分析
Reducto 的优势:准确性和生产就绪性
Reducto 针对需要极高准确性的高价值、高吞吐量的生产环境(如金融、医疗、法律)进行了优化。其设计流程——先进行 CV 解析,再进行 VLM 解释和 Agentic 模型校正——表明它是一个旨在最大限度减少提取错误的强大系统。它明确强调企业级功能,如安全合规性 (SOC2, HIPAA) 和灵活的部署选项(可在用户自己的基础设施中运行),使其成为寻求可靠 API 服务的成熟组织的首选。
RAG-Anything 的优势:语义深度和灵活性
RAG-Anything 的核心优势在于其 All-in-One RAG 框架方法 和先进的语义结构化能力。通过构建多模态知识图谱,它超越了简单的分块或总结,明确地对不同模态(文本、图像、表格、公式)之间的关系进行建模。这种关系一致性在检索过程中得以保持,确保信息传递是上下文整合的。此外,VLM 增强查询模式 允许在查询阶段对检索到的视觉内容进行动态、实时的 VLM 分析,这对于需要 VLM 在上下文中对图表进行即时解释的用例非常有用。它还支持直接插入预解析的内容列表,提供了高度的灵活性和可定制性。
应用建议
选择 Reducto 还是 RAG-Anything 主要取决于用户的操作环境、技术要求和最终目标:
Reducto 推荐场景
如果用户需要满足以下条件,则推荐使用 Reducto:
- 极高的提取准确性: 主要目标是从复杂文档(如财务报告或法律文件)中提取高度可靠的结构化数据,其中微小的解析错误代价高昂。
- 企业级生产要求: 应用需要高可用性 (99.9%+ uptime)、严格的安全合规性 (HIPAA, SOC2),或需要在私有环境中部署。
- 偏好 API 集成: 用户倾向于集成一个经过管理、具备服务水平协议 (SLAs) 的商业 API 服务,而不是维护一个复杂的开源框架及其依赖项。
RAG-Anything 推荐场景
如果用户需要满足以下条件,则推荐使用 RAG-Anything:
- 深度的关系理解: 应用程序依赖于理解多模态组件之间的语义关系和层次结构,例如在学术研究或技术文档中,上下文至关重要。多模态知识图谱能力 在此特别适用。
- 高度定制和控制: 用户需要对处理流程、解析器(MinerU/Docling) 和检索机制进行精细控制,并可能希望实施自定义模态处理器。
- 动态 VLM 查询分析: 对于查询结果受益于检索时对视觉组件进行实时 VLM 分析的用例,例如要求 LLM 根据检索到的特定图像来“分析文档中的图表和数字”。
- 处理复杂的数学内容: 文档中经常包含复杂的数学表达式和公式,需要原生 LaTeX 格式解析和概念映射。
Comparison and Analysis of Reducto and RAG-Anything
Both Reducto and RAG-Anything leverage Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to enhance the understanding of multimodal documents, ensuring that non-textual content like images and tables are converted into LLM-ready data or integrated contextually for deeper insights. However, they differ significantly in their architecture, purpose, and VLM implementation focus.
1. Architectural Focus and System Nature
| Feature | Reducto | RAG-Anything |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Commercial product/service, characterized as an “AI document parsing & extraction software” offered via flexible APIs. | Open-source RAG framework, described as a “comprehensive All-in-One Multimodal Document Processing RAG system” built on LightRAG. |
| Core Pipeline | Uses a multi-pass system starting with Traditional Computer Vision (layout-aware models) for document breakdown, followed by VLM interpretation and VLM/Agentic model corrections. | Implements a multi-stage multimodal pipeline (Document Parsing → Content Analysis → Knowledge Graph → Intelligent Retrieval). |
| Enterprise Readiness | Built for production AI, trusted by Fortune 10 enterprises, with 99.9%+ uptime, Enterprise support, and certifications (SOC2, HIPAA compliant). Can be deployed entirely within the user’s infrastructure. | Focuses on providing a flexible, integrated RAG framework. Requires user setup for dependencies (e.g., LibreOffice for Office documents) and external models (e.g., OpenAI’s GPT-4o for VLM functions). |
2. VLM Utilization and Multimodal Processing
Both platforms use VLMs to bridge the gap between visual information and textual context, but they deploy them at different stages or for different primary goals:
Reducto’s VLM Approach (Correction and Interpretation)
Reducto’s system uses VLMs primarily during the content analysis and refinement phases of document extraction.
- Layout Segmentation (CV First): Traditional computer vision models first break down the document visually, identifying regions, tables, figures, and text.
- Contextual Interpretation (VLM): VLMs then interpret each identified region in context. This is critical for tasks like linking labels to values, understanding complex tables, and classifying segments.
- Accuracy Enhancement (Agentic Model/VLM): Reducto features an Agentic model—which performs like a human editor—to detect minor mistakes and correct them, ensuring accuracy even in detailed cases. Reducto aims to produce the most accurate, LLM-ready results.
RAG-Anything’s VLM Approach (Generation and Retrieval)
RAG-Anything utilizes VLMs both during the initial content processing stage and, notably, during the query stage:
- Processing (Visual Content Analyzer): A dedicated Visual Content Analyzer integrates vision models to generate context-aware descriptive captions based on visual semantics. It also extracts spatial relationships and hierarchical structures between visual elements.
- Querying (VLM-Enhanced Query Mode): RAG-Anything now features a VLM-Enhanced Query mode. When documents containing images are queried, the system automatically:
- Retrieves relevant context containing image paths.
- Loads and encodes the images as base64.
- Sends both the text context and the images directly to the VLM (e.g., GPT-4o) for comprehensive analysis during retrieval/answering. This allows the VLM to combine visual and textual context for deeper insights. This mode can be automatically or manually enabled/disabled.
- Multimodal Querying: RAG-Anything also supports specific Multimodal Queries where the user provides specific content (like table data or a LaTeX formula) alongside the query for enhanced analysis.
3. Output Structure and Content Scope
Both systems aim to structure data for LLMs, but RAG-Anything places a heavy emphasis on relationship mapping:
Data Structuring
- Reducto: Focuses on extracting data into LLM-optimized formats, including intelligent chunking, figure summarization, graph extraction, and embedding optimization. The goal is to transform unstructured documents into structured, reliable data.
- RAG-Anything: Transforms document content into structured semantic representations via a Multimodal Knowledge Graph Index. This process involves Multi-Modal Entity Extraction (with semantic annotations) and crucial Cross-Modal Relationship Mapping (establishing dependencies between textual entities and multimodal components). This framework uses hybrid retrieval combining vector search and graph traversal algorithms.
Supported Content Types
- Reducto: Supports PDFs, images, spreadsheets, slides. It handles complex documents like investor decks, SEC filings, dense pitch materials, complex tables, charts, and financial statements. It offers multilingual parsing across 100+ languages.
- RAG-Anything: Provides dedicated processors for images, tables, and mathematical equations (supporting native LaTeX format). It supports a wide range of document formats (PDFs, Office Documents, Images, Text Files). It also features an Extensible Modality Handler for custom and emerging content types.
Detailed Analysis
Reducto’s Strength: Accuracy and Production Readiness Reducto appears optimized for high-stakes, high-volume production environments where extraction accuracy is paramount (e.g., finance, healthcare, legal). Its reliance on an initial CV pass followed by VLM interpretation and, critically, VLM-based Agentic correction suggests a robust system designed to minimize errors inherent in initial parsing. The explicit focus on enterprise features (SLAs, security compliance, deployment options) makes it suitable for large organizations seeking a reliable, ready-to-use API.
RAG-Anything’s Strength: Semantic Depth and Flexibility RAG-Anything’s strength lies in its All-in-One RAG framework approach and its advanced semantic structuring. By constructing a Multimodal Knowledge Graph, it goes beyond simple chunking or summarization to explicitly model the relationships between different content modalities (text, images, tables, equations). This relational coherence is maintained during retrieval, ensuring contextually integrated information delivery. Furthermore, the innovative VLM-Enhanced Query mode allows for dynamic, real-time VLM analysis of retrieved images during the final query phase, enabling deeper insights based on the retrieved context. The system also offers flexibility through multiple parser options (MinerU, Docling) and the ability to insert pre-parsed content lists.
Application Recommendations
The choice between Reducto and RAG-Anything depends heavily on the user’s operational context, technical requirements, and end goal:
Recommendation for Reducto
Reducto is recommended when the user requires:
- Maximum Extraction Accuracy: If the primary goal is highly reliable, structured data extraction from complex documents (like financial reports or legal filings) where even minor parsing errors are costly.
- Enterprise Production Readiness: If the application requires high availability, dedicated enterprise support (SLAs), strict security compliance (HIPAA, SOC2), or deployment within a private environment.
- API Integration Preference: If the user prefers integrating a streamlined, managed service via API rather than maintaining an open-source framework and its dependencies.
Recommendation for RAG-Anything
RAG-Anything is recommended when the user requires:
- Deep Relational Understanding: If the application relies on understanding semantic relationships and hierarchical structure between multimodal components, such as in academic research or technical documentation where context is crucial. The Multimodal Knowledge Graph capability is ideal here.
- Customization and Control: Since RAG-Anything is an open-source framework built on LightRAG, it is suitable for users who need fine-grained control over the processing pipeline, parsers (MinerU/Docling), retrieval mechanisms, and who may want to implement custom modal processors.
- Dynamic VLM Querying: For use cases where query results benefit from real-time VLM analysis of retrieved visual components, such as asking an LLM to “Analyze the charts and figures in the document” based on the specific images retrieved for the context.
- Handling Mathematical Content: If documents frequently contain complex mathematical expressions and formulas that require native LaTeX format parsing and conceptual mapping.