Google Research近日提到,在其从事连接组学(Connectomics,一门研究神经元之间连接模式的科学,旨在揭示大脑功能和行为的基础)研究十年之后,其实才刚刚开始。展望未来,谷歌研究团队与哈佛大学及其他机构的合作伙伴正在努力绘制小鼠海马体的图谱,海马体是大脑中与学习和记忆相关的部分。了解多种生物的大脑是如何连接的,可以帮助研究人员更好地理解阿尔茨海默病等神经系统疾病,并回答诸如记忆如何形成等基本问题。
线虫有302个神经元,其连接图谱于1986年建立;果蝇有10,000个神经元,其连接图谱于2020年建立。小鼠有71,000,000个神经元,其连接图谱正在研究和创建中…,完成的时间待定(20XX)。人类脑部有86,000,000,000个神经元,其全连接图谱创建完成时间可能为数百年之后(2XXX)。不过,科学研究常常无法预测,一旦取得某个突破性成果,相关研究的可能会指数级加速。

相关视频(视频内容总结由Google Gemini生成)如下:
该视频讲述了连接组学,即绘制生物体神经细胞之间所有连接的图谱。视频主讲人来自谷歌研究,他讨论了创建连接组学面临的挑战以及拥有连接组学的潜在好处。
视频首先解释了理解大脑的困难。尽管有许多神经生物学家研究大脑,但我们仍然对它的工作原理了解甚少。连接组学是一门旨在创建生物体连接组学的学科。第一个连接组学是由一种叫做秀丽隐杆线虫的线虫创建的,它只有300个神经元。研究人员花了10年时间才创建了这个连接组学,这使得研究人员多年来不敢创建更复杂生物体的连接组学。
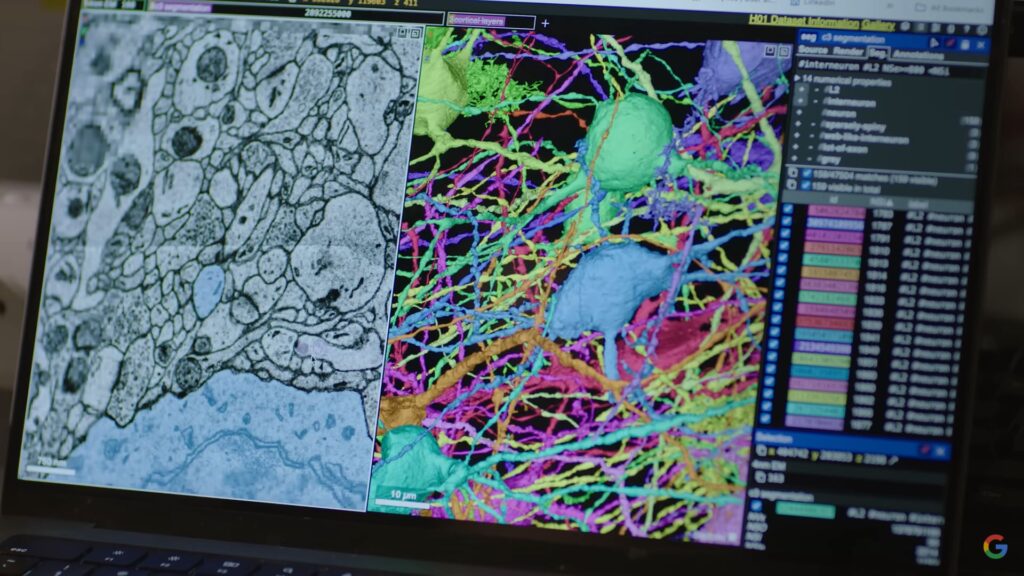
最近的技术进步使得创建更复杂生物体的连接组学成为可能。主讲人讨论了创建果蝇大脑连接组学的过程。该过程涉及使用电子显微镜拍摄大脑切片的超高分辨率图像。然后将这些图片拼接在一起以创建大脑的3D图像。然后,使用软件来跟踪大脑中神经元之间的连接。
主讲人还讨论了创建小鼠大脑连接组学的挑战。小鼠大脑比果蝇大脑大1000倍,而且复杂得多。然而,小鼠大脑仍然比人类大脑小得多。主讲人认为,如果我们能够创建小鼠大脑的连接组学,我们将会学到很多关于大脑工作原理的知识,以至于不需要创建人类大脑的连接组学。
视频最后讨论了连接组学的潜在好处。主讲人认为,连接组学将帮助我们理解记忆是如何形成的以及如何识别精神疾病。为了创建连接组学,我们需要继续开发新技术。
This video talks about a connectome, which is a map of all the connections between nerve cells in an organism. The speaker of the video, a researcher from Google Research, discusses the challenges of creating a connectome and the potential benefits of having one.
The video starts by explaining how difficult it is to understand the brain. Even though there are many neurobiologists studying the brain, we still have a poor understanding of how it works. Connectomics is a field of study that aims to create a connectome of an organism. The first connectome was created of a worm called C. elegans, which has only 300 neurons. It took researchers 10 years to create this connectome, and this discouraged researchers from creating connectomes of more complex organisms for many years.
Recent technological advancements have made it possible to create connectomes of more complex organisms. The speaker discusses the process of creating a connectome of a fruit fly brain. This process involves taking high-resolution pictures of slices of the brain using electron microscopes. These pictures are then stitched together to create a 3D image of the brain. Then, software is used to trace the connections between the neurons in the brain.
The speaker also discusses the challenges of creating a connectome of a mouse brain. A mouse brain is 1,000 times larger than a fruit fly brain, and it is much more complex. However, a mouse brain is still much smaller than a human brain. The speaker believes that if we can create a connectome of a mouse brain, we will be able to learn so much about how brains work that we will not need to create a connectome of a human brain.
The video concludes by discussing the potential benefits of connectomes. The speaker believes that connectomes will help us to understand how memories are formed and how to recognize mental disorders. In order to create connectomes, we need to continue to develop new technologies.